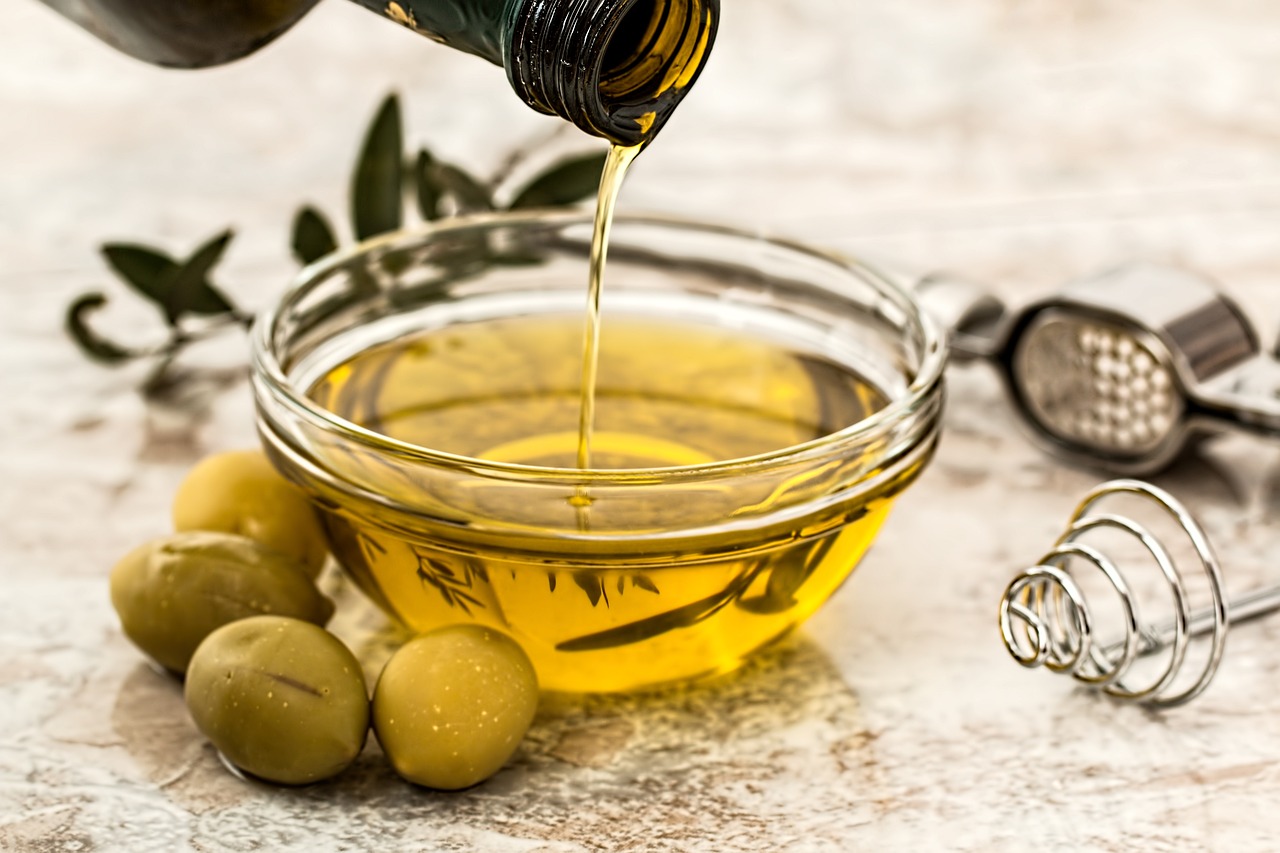
Olive oil offers healthier fats and a distinct flavor, while Butter enriches cooking. In Europe, olive oil is common for Mediterranean cuisine, while Butter is prominent in Northern European dishes.
Olive oil and Butter are two essential ingredients that play a significant role in European cuisine. Throughout history, olive oil and Butter have been utilized in many European dishes, providing distinct flavors and textures.
Olive oil is prominent in Mediterranean culinary traditions, while Butter is a staple in Western European gastronomy. These ingredients have shaped the flavors of European dishes and become integral to the cultural identity of various regions across the continent.
In this blog post, we’ll compare the uses, benefits, and cultural significance of olive oil and Butter in European culinary traditions.
Olive Oil Europe Vs Butter Europe – Their Role in European Cooking
The choice between olive oil and Butter in Europe depends on culinary preferences, health considerations, and intended use.
Olive oil offers heart-healthy fats, antioxidants, and a distinct flavor, making it a staple in Mediterranean cuisine. Butter, with its rich taste and creamy texture, butter is favored in Northern European cooking and adds indulgence to baked goods and sauces.
Here are the Distinctions between olive oil and Butter to understand their role in cooking.
Olive Oil Usage in Europe:

Culinary Tradition:
- A fundamental element of Mediterranean cuisine is olive oil.
- Mediterranean countries like Italy, Greece, Spain, and Southern France use it extensively.
Health Benefits:
- The monounsaturated fats in olive oil makes it good for your heart’s health.
- It contains antioxidants and vitamins, contributing to overall well-being.
Flavor Profile:
- Olive oil offers a fruity and sometimes peppery flavor.
- It enhances dishes with a unique taste and is commonly used in salads and dips.
Smoke Point:
- Due to the higher smoke point compared to Butter, olive oil is appropriate for high-heat cooking methods such as frying.
Culinary Versatility:
- Used for cooking, dressing, marinating, and as a finishing touch to dishes.
Butter Usage in Europe:
Culinary Tradition:
- Butter holds significance in Northern European cooking.
- It is commonly used in countries like France, Germany, the UK, and Scandinavia.
Richness and Flavor:
- Butter adds a creamy and savory taste to food.
- It’s preferred for baked goods, sauces, and dishes where a rich flavor is desired.
Nutritional Composition:
- Butter contains substantial amounts of saturated fats, which, when consumed excessively, can have an impact on cholesterol levels.
Smoke Point:
- With a lower smoke point than olive oil, Butter’s application in high-heat cooking is restricted.
Cultural Heritage:
- Traditional European recipes often call for Butter in classic dishes and pastries.
The choice between olive oil and Butter in European cuisine reflects regional culinary preferences, health considerations, and the desired flavor profiles in different dishes.
A comparison Table – Olive oil Europe Vs. butter Europe
Here’s a comparison between olive oil and Butter in European cuisine, highlighting their differences in a table:
| Aspect | Olive Oil | Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from olives | Made from cream, usually from cow’s milk |
| Types | Extra virgin, virgin, refined, pomace, etc. | Salted, unsalted, cultured, clarified, etc. |
| Flavor Profile | Fruity, mild, sometimes peppery | Rich, creamy, can be slightly tangy |
| Health Benefits | High in monounsaturated fats, antioxidants | Contains saturated fats, cholesterol |
| Nutritional Value | Rich in vitamins E and K, low in saturated fats | Contains vitamins A, D, E, and K, saturated fats |
| Cooking Use | Versatile for various cooking methods | Used for sautéing, baking, and flavoring |
| Cooking Temperatures | High smoke point suitable for frying | The lower smoke point can burn at high heat |
| Culinary Applications | Salad dressings, sautéing, roasting, grilling | Baking, cooking, flavoring, pastries |
| Regional Usage | Prominent in Mediterranean and Southern Europe | Common in Northern European cuisines |
| Cultural Significance | Part of Mediterranean diet and lifestyle | A traditional ingredient in many European dishes |
| Storage | Store away from light and heat; dark bottles | Requires refrigeration to prevent spoilage |
| Dietary Restrictions | Suitable for vegetarians and vegans | Not suitable for lactose-intolerant vegans |
Remember that while this table provides a general overview of the differences between olive oil and Butter in European cuisine, culinary practices and preferences can vary widely within different regions and cultures across Europe.
How is olive oil used in European cuisine?
Olive oil is prominent in European cuisine, playing a vital role in enhancing flavors and textures across various dishes. Its versatility and health benefits have led to its widespread use throughout the continent.
Here’s how olive oil is utilized in European cuisine, explained in points:
Cooking Medium
Olive oil serves as a fundamental cooking medium in many European cuisines. Due to the high smoke point, Olive oil is used for sautéing, frying, and even deep-frying. The oil’s fruity and mild flavor enhances the taste of dishes without overwhelming other ingredients.
Salad Dressing
Olive oil is a key ingredient in crafting traditional European salad dressings. Mixed with vinegar, lemon juice, or other acids, it forms the base of vinaigrettes that are drizzled over various salads.
Its smooth texture helps emulsify the dressing for a well-balanced flavor.
Dipping and Dipping Sauces
In Mediterranean countries like Italy and Spain, olive oil is often served as a dip for bread. It can also be infused with herbs, spices, or garlic to create flavorful dipping sauces accompanying bread, vegetables, or other appetizers.
Pesto and Sauces
Olive oil is a vital component in making pesto, a sauce originating from Italy. It binds ingredients like basil, pine nuts, garlic, and Parmesan cheese, resulting in a luscious and aromatic sauce.
Olive oil is also used in pasta sauces to enhance the overall richness and silkiness.
Marinades
European cuisines frequently use olive oil as a base for marinades. Meats, seafood, and vegetables are soaked in marinades containing olive oil, herbs, spices, and other seasonings. The oil helps tenderize and infuse flavors into the ingredients.
Grilling and Roasting
Olive oil is brushed onto meats, fish, and vegetables before grilling or roasting. Adding moisture and preventing sticking, brushing olive oil enhances the taste of your dish.
Baking
In some European desserts and pastries, olive oil is used as a substitute for Butter or other fats. Its distinctive flavor profile can add a unique twist to baked goods, resulting in a more complex and interesting taste.
Preservation
Olive oil has been used for centuries as a method of food preservation, especially in the form of infused oils. Herbs, spices, and aromatics are added to the oil, creating flavorful mixtures that can be used in various dishes.
Drizzling and Finishing
High-quality extra virgin olive oil is often drizzled over finished dishes just before serving. This imparts a final burst of flavor and adds an appealing sheen to the presentation.
Regional Specialties
Different European regions have their unique ways of using olive oil. For instance, in Mediterranean cuisine, olive oil is a cornerstone ingredient in dishes like Greek moussaka and Spanish paella.
Overall, olive oil’s adaptability, nutritional value, and rich history have solidified its place as an essential ingredient in European cuisine, contributing to the diverse and flavorful dishes found across the continent.
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks Associated with Olive Oil Europe vs. Butter Europe?

Benefits of Olive Oil in Europe:
Heart-Healthy Fats:
- With enriched monounsaturated fats, olive oil is recognized for its potential benefits to heart health.
- These fats can potentially decrease LDL cholesterol levels and mitigate the risk of heart disease.
Antioxidants and Nutrients:
- Vitamin E, antioxidant properties, and nutrients in olive oil add to the human’s health benefits.
- These compounds have anti-inflammatory effects and support overall well-being.
Mediterranean Diet Benefits:
- Olive oil constitutes a fundamental aspect of the Mediterranean diet, linked to reduced incidences of chronic diseases and an extended life expectancy.
- The diet emphasizes whole foods, vegetables, and healthy fats, contributing to improved health outcomes.
Distinctive Flavor:
- Olive oil adds a unique fruity and sometimes peppery flavor to dishes.
- It enhances salads, dips, and Mediterranean-inspired recipes with a pleasant taste.
Drawbacks of Olive Oil in Europe
Caloric Density:
- Olive oil is calorie-dense, so excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain if not used in moderation.
Limited High-Heat Cooking:
- While it has a higher smoke point than Butter, olive oil’s high-quality nutrients might degrade when exposed to high heat.
Benefits of Butter in Europe:
Rich Flavor and Texture:
- Butter adds a creamy, luxurious taste to dishes, enhancing the overall dining experience.
- It’s a key ingredient in baked goods, sauces, and comfort foods.
Vitamins and Nutrients:
- The presence of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K in Butter is vital for a variety of bodily functions.
Cultural Significance:
- Butter is a traditional element of European cuisine, contributing to the authenticity of many classic recipes.
Drawbacks of Butter in Europe:
Saturated Fat Content:
- When consumed excessively, butter is high in saturated fats. The fat can raise bad cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk.
Smoke Point Limitation:
- Due to its lower smoke point, Butter is not ideal for high-heat cooking methods.
In Europe, choosing olive oil and Butter involves weighing these benefits and drawbacks to align with culinary preferences, dietary considerations, and health goals.
What Factors Influence The Choice Between Olive Oil And Butter In Europe?
The choice depends on the dish, the desired flavor profile, and health considerations. European culinary practices often prioritize using locally available ingredients and traditional techniques to create balanced and flavorful dishes.
Culinary Tradition and Cuisine:
- Olive Oil: Mediterranean countries have a historical connection with olive oil, using it as a base for their dishes.
- Butter: Northern European countries have a tradition of using Butter due to their colder climate, influencing their cuisine.
Health Considerations:
- Olive Oil: The Monounsaturated fats in olive oil make it supportive to the heart and connected with the advantages of the Mediterranean diet.
- Butter: Contains saturated fats, which, when consumed in excess, can impact cholesterol levels and heart health.
Flavor Profiles:
- Olive Oil: Offers a distinctive fruity taste that complements salads, dips, and lighter dishes.
- Butter: Imparts a creamy, savory flavor that enhances baked goods, sauces, and dishes desiring richness.
Culinary Versatility:
- Olive Oil: Suitable for various cooking methods, including frying, sautéing, dressing, and marinades.
- Butter: Often preferred for baking, where its texture and flavor contribute to desirable results.
Smoke Points:
- Olive Oil: With a higher smoke point, olive oil is more suitable for high-heat cooking without undergoing breakdown.
- Butter: Lower smoke point limits its use in high-temperature cooking.
Cultural Heritage:
- Olive Oil: Symbolizes the Mediterranean lifestyle and its associated health benefits.
- Butter: Represents the traditional richness of European cuisines, especially in comfort foods.
Dietary Choices:
- Olive Oil: Often chosen by those prioritizing plant-based and heart-healthy diets.
- Butter May be favored by those who value flavor and indulgence in moderation.
Recipe Requirements:
- Olive Oil: Preferred in recipes that emphasize freshness and lighter flavors.
- Butter: Ideal for recipes needing a creamy texture and deeper taste.
The choice between olive oil and Butter is influenced by a combination of these factors, allowing individuals to align their cooking and dietary preferences with the unique characteristics of each option.
FAQs
1. Are there cultural preferences for olive oil or Butter in Europe?
Yes, there are cultural preferences. Mediterranean cuisines lean heavily toward olive oil, while countries like France have a strong butter tradition. However, globalization has led to more cross-cultural culinary influences.
2. What are the benefits of using olive oil in cooking?
Abundant in antioxidants and healthy fats, olive oil becomes a heart-healthy option. It’s associated with reducing inflammation and promoting good cholesterol levels.
3. How does butter feature in European culinary traditions?
Butter plays a significant role in European cooking, especially in France and Northern Europe. It’s used for baking, sautéing, and enhancing flavors in various dishes.
4. Are there health considerations when using Butter?
Yes, Butter is high in saturated fats and cholesterol, which can impact heart health when consumed excessively. Moderation is key, and some European cuisines balance butter use with other healthier fats.
5. How does olive oil differ from Butter regarding smoke points?
Due to the lower smoke point compared to numerous cooking oils, olive oil is appropriate for medium-heat cooking. Butter’s smoke point can vary based on its type, but it generally has a lower smoke point than many cooking oils and is better for lower-heat cooking.
6. Which is more commonly used for European baking: olive oil or Butter?
In many European baking traditions, Butter is the preferred fat due to its creamy texture and ability to create tender baked goods. Olive oil is used in specific recipes, often in Mediterranean-style baked goods.
7. How do the flavors of olive oil and Butter compare?
Olive oil has a distinct fruity, sometimes peppery flavor that can enhance salads and Mediterranean dishes. Butter has a rich, creamy taste that adds depth to both sweet and savory dishes.
8. Can olive oil and Butter be used interchangeably in recipes?
Yes, olive oil and Butter can be used interchangeably in recipes, but their unique flavors and different smoke points should be considered for the best outcome.
Conclusion
Whether you are a food enthusiast or simply curious about European cuisine, this blog post will guide you to better appreciate and differentiate between these two beloved ingredients – Olive oil and Butter Europe.
By examining their roles in different cuisines, we hope to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the unique attributes and contributions of both olive oil and Butter in European cooking.