The impact of the ketogenic diet on the immune system is still being studied, and the evidence is limited, but some studies suggest that it may have beneficial effects. The ketogenic diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is important for a healthy immune system. It can also improve the function of certain immune cells, including T cells and natural killer cells, which play a vital role in fighting off infections and diseases of the common STDs.
However, the long-term effects of the ketogenic diet on the immune system are still unknown, and more research is needed to understand the relationship between diet and immunity fully. It’s also important to note that while the diet may have some potential benefits, it should not be used as a replacement for traditional medical treatment and should only be followed under the supervision of a doctor.
What is a ketogenic diet?
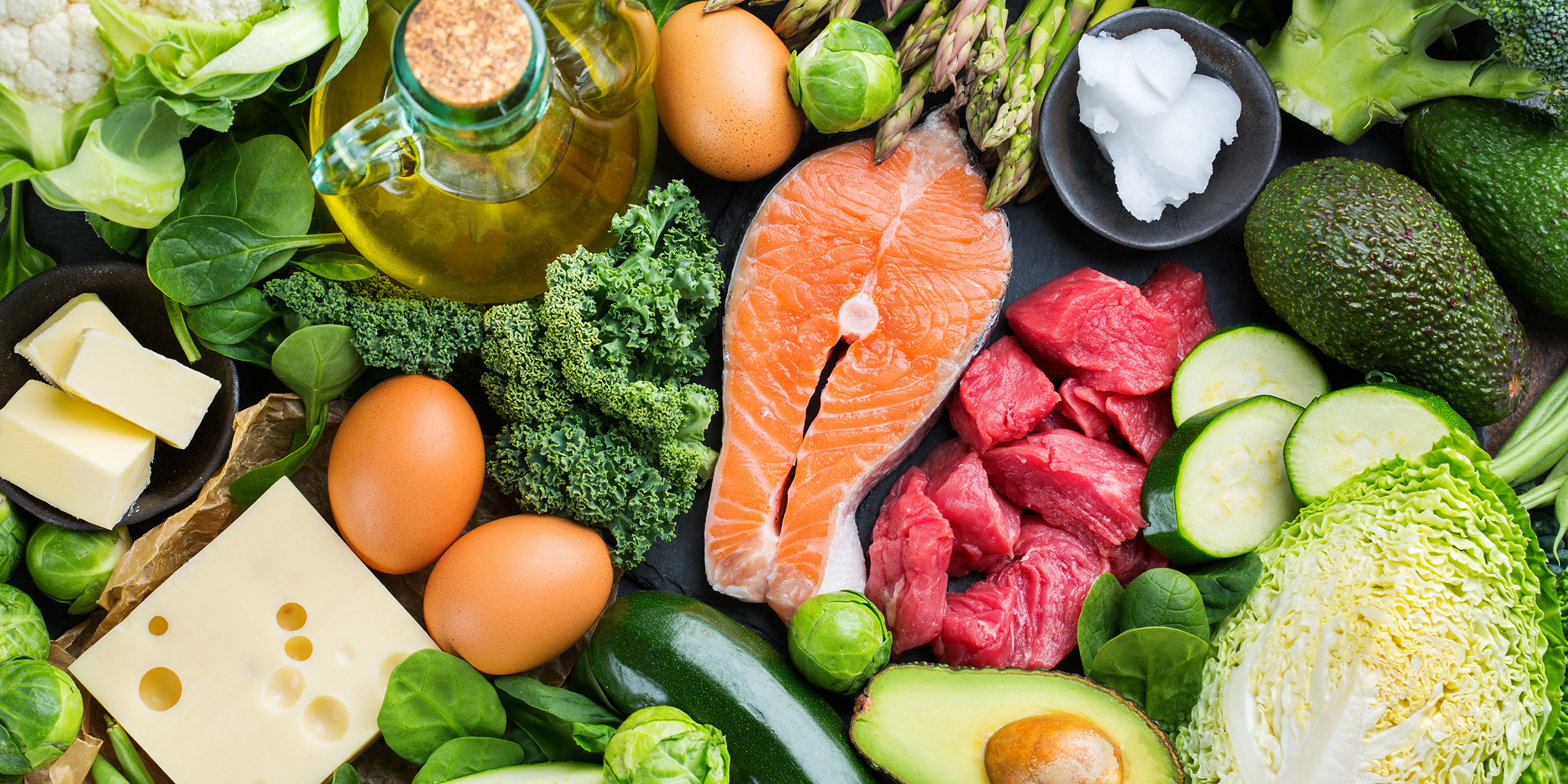
The ketogenic diet (often called keto) is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has been claimed to help people lose weight. The idea behind the diet is to get your body into a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. To do this, you need to severely limit your carbohydrate intake and eat a diet high in healthy fats.
This can include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, oils and fats, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. The diet is sometimes used to treat certain medical conditions, but its effects on overall health and long-term weight loss are still being studied.
How does the ketogenic diet affect the immune system?
The effects of the ketogenic diet on the immune system are still poorly understood, as research in this area is limited and often conflicting. However, some studies suggest that diet may positively and negatively affect the immune system.
Positive effects:
- Reduces inflammation: The ketogenic diet has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body, which is important for a healthy immune system.
- Improves immune cell function: Some studies suggest that the diet may improve the function of certain immune cells, such as T cells and natural killer cells, which play a crucial role in fighting off infections and diseases.
Negative effects:
- Decreased immune function: Other studies have shown that the ketogenic diet may suppress the immune system and decrease the body’s ability to fight infections and diseases.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies: The ketogenic diet may also lead to deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins D and B12, that are important for a healthy immune system.
What to eat on a keto diet?
The following foods are typically consumed on a ketogenic diet:
- Meat and poultry: Beef, chicken, pork, etc.
- Fish and seafood: Salmon, shrimp, trout, etc.
- Eggs: Whole eggs or egg whites.
- Dairy products: Cheese, heavy cream, butter, etc.
- Oils and fats: Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, etc.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, chia seeds, etc.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, etc.
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, etc. (in moderation due to their sugar content)
Avoid or limit foods high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, rice, sugary drinks, and sweetened snacks. These foods can quickly kick you out of ketosis and should be limited or avoided on a ketogenic diet. It’s also important to focus on eating whole, unprocessed foods and to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian before starting the diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the research on the ketogenic diet and the immune system is limited, and more research is needed to understand the relationship between the two fully. It’s also important to consult with a doctor before starting the diet, as it may not be appropriate for everyone and may interact with certain medications or medical conditions.